Blanking Force
Calculation of Blanking Force: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Blanking Force in Metal Stamping
 The calculation of blanking force represents a fundamental aspect of metal stamping processes, determining both the quality of finished products and the selection of appropriate machinery. As China Custom Stamping, a professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturer in China, we understand that precise force calculation forms the backbone of efficient production and cost-effective operations in the sheet metal industry.
The calculation of blanking force represents a fundamental aspect of metal stamping processes, determining both the quality of finished products and the selection of appropriate machinery. As China Custom Stamping, a professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturer in China, we understand that precise force calculation forms the backbone of efficient production and cost-effective operations in the sheet metal industry.
Blanking force refers to the total resistance encountered during the punching or blanking process, comprising several distinct components that must be carefully calculated to ensure optimal press selection and tooling design. This comprehensive guide explores the theoretical foundations, practical calculation methods, and advanced techniques for force reduction in modern stamping operations.
Components of Blanking Force
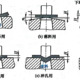
The total blanking force (F₀) consists of four primary elements that occur at different stages of the punching process:
-
Blanking Force (F): The principal force required to shear the material, representing approximately 70-80% of total force requirements. This initial shear force depends on material properties, thickness, and cutting perimeter.
-
Stripping Force (Fs): The additional force needed to remove the scrap material or finished part from the punch after penetration. This typically accounts for 3-10% of the blanking force.
-
Pushing Force (Fp): The energy required to eject the blanked material through the die opening. This varies based on die design and material springback characteristics.
-
Counterblanking Force (Fc): In some operations, an upward force is necessary to remove parts from the die cavity, especially in inverted tooling setups.
China Custom Stamping, as a professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturer in China, emphasizes the importance of calculating each component separately before combining them for total force requirements. The general formula for total blanking force is:
F₀ = F + Fs + Fp + Fc
Detailed Calculation Methods
1. Blanking Force Calculation
The fundamental blanking force calculation follows two primary approaches depending on tooling geometry:
A. Straight-edge Tooling Calculation
F = 1.3 × L × t × τ
or
F ≈ L × t × σ_b
Where:
-
F: Blanking force (N)
-
L: Perimeter length of blanked feature (mm)
-
t: Material thickness (mm)
-
τ: Material shear strength (MPa)
-
σ_b: Material tensile strength (MPa)
-
1.3: Safety factor accounting for tool wear, lubrication, and material variations
B. Angled-edge Tooling Calculation
F_angled = K_reduction × F
Where:
-
K_reduction: Force reduction coefficient (see Table 1)
-
F: Straight-edge blanking force
Table 1: Force Reduction Coefficients for Angled Tooling
| Angle (°) | Reduction Coefficient (K_reduction) | % of Straight-edge Force |
|---|---|---|
| <5 | 0.30-0.40 | 30-40% |
| 5-8 | 0.60-0.65 | 60-65% |
| 8-12 | 0.70-0.80 | 70-80% |
At China Custom Stamping, our professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturing team in China utilizes both methods depending on production requirements—straight-edge for precision cutting and angled-edge for force reduction in high-tonnage applications.
2. Auxiliary Force Calculations
A. Stripping Force (Fs)
Fs = ks × F
B. Pushing Force (Fp)
Fp = n × kp × F
where n = h/t (h: die straight wall height; t: material thickness)
C. Counterblanking Force (Fc)
Fc = kc × F
Table 2: Force Coefficients for Different Materials
| Material Thickness (mm) | ks (Steel) | kp(Steel) | kc (Steel) | Aluminum Alloys | Copper/Brass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤0.1 | 0.10 | 0.065-0.075 | 0.14 | 0.025 | 0.02-0.06 |
| 0.1-0.5 | 0.063 | 0.045-0.055 | 0.08 | 0.025-0.08 | 0.03-0.07 |
| 0.5-2.5 | 0.055 | 0.04-0.05 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.03-0.09 |
| 2.5-6.5 | 0.045 | 0.03-0.04 | 0.05 | – | – |
| >6.5 | 0.035 | 0.02-0.03 | 0.04 | – | – |
Practical Calculation Example
Consider a China Custom Stamping project requiring blanking of 3mm thick stainless steel (τ=520MPa, σ_b=650MPa) with a rectangular profile (100mm × 50mm):
-
Perimeter Calculation:
L = 2×(100+50) = 300mm -
Blanking Force:
F = 1.3×300×3×520 = 608,400N ≈ 608.4kN
or
F ≈ 300×3×650 = 585,000N ≈ 585kN -
Auxiliary Forces (from Table 2):
ks=0.055, kp=0.045, kc=0.06
Assuming n=5 (die height=15mm)
Fs = 0.055×585 = 32.2kN
Fp = 5×0.045×585 = 131.6kN
Fc = 0.06×585 = 35.1kN -
Total Force:
F₀ = 585 + 32.2 + 131.6 + 35.1 = 783.9kN -
Press Selection:
Recommended press capacity = 1.3×783.9 ≈ 1019kN (≈104 metric tons)
This example demonstrates how China Custom Stamping, as a professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturer in China, approaches real-world force calculations to ensure proper equipment selection.
Advanced Considerations in Force Calculation
Material Property Variations
Modern metal stamping operations must account for:
-
Anisotropic Materials: Grain direction affects shear resistance
-
Tempered Alloys: Hardness variations through material thickness
-
Composite Materials: Non-homogeneous structures require modified calculations
Dynamic Loading Conditions
High-speed presses (600+ SPM) introduce inertial effects that may increase apparent blanking force by 15-25%. China Custom Stamping’s professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturing facilities in China incorporate dynamic correction factors for high-volume production.
Tool Wear Compensation
As cutting edges wear (typically after 50,000-100,000 strokes), blanking force may increase by 20-30%. Progressive die operations require periodic force reassessment.
Force Reduction Techniques
1. Angled Tooling Implementation
Implementing 5-12° shear angles can reduce peak force by 30-70%, as demonstrated in the angled-edge calculation method. China Custom Stamping’s professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturing engineers in China often employ:
-
Single-side Angling: For asymmetrical parts
-
Dual-side Angling: For balanced force distribution
-
Stepped Angling: For complex geometries
2. Progressive Blanking
Dividing the blanking process into multiple steps:
-
Nibbling: Sequential small punches
-
Step Blanking: Gradual perimeter reduction
-
Slug Control: Managed material separation
3. Material Optimization
-
Annealing: Softening materials pre-forming
-
Localized Heating: Reducing shear resistance in critical areas
-
Lubrication Strategies: Advanced tribological solutions
4. Press Synchronization
China Custom Stamping’s professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturing teams in China coordinate:
-
Cushion Systems: For controlled stripping
-
Ejection Timing: To minimize simultaneous force peaks
-
Load Monitoring: Real-time force adjustment
Industry Applications
Automotive Components
Blanking force calculations for door panels (typically 800-1200 tons) require precise edge quality considerations. China Custom Stamping’s professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturing solutions for automotive clients incorporate:
-
Tailored Blank Calculations: Mixed thickness materials
-
High-Strength Steel Factors: Advanced material models
-
Crash-Relevant Edge Quality: Controlled fracture zones
Electronics Enclosures
Precision thin-gauge stamping (0.1-0.5mm) demands:
-
Micro-Blanking Formulas: Scale-adjusted coefficients
-
Burr Control Factors: Edge quality modifications
-
Fine Blanking Considerations: Triple-action press calculations
Appliance Manufacturing
Large-area blanking (refrigerator panels, oven doors) involves:
-
Contour-Dependent Calculations: Irregular perimeter adjustments
-
Texture Effects: Surface pattern influences
-
Coated Material Factors: Pre-painted steel considerations
Future Trends in Blanking Force Calculation
AI-Powered Predictive Models
China Custom Stamping, as a forward-thinking professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturer in China, is developing:
-
Machine Learning Algorithms: For material behavior prediction
-
Digital Twin Simulations: Virtual process optimization
-
Real-Time Adaptive Control: Dynamic parameter adjustment
Advanced Material Science
Emerging materials require:
-
Composite Material Models: Hybrid calculation methods
-
Nanostructured Alloys: Microstructure-based formulas
-
Smart Material Considerations: Shape memory effects
Sustainable Manufacturing
Force calculation now incorporates:
-
Energy Efficiency Metrics: kWh per ton calculations
-
Waste Reduction Models: Optimal blank nesting
-
Tool Life Extensions: Wear-compensated formulas
Conclusion
The precise calculation of blanking force remains a cornerstone of efficient metal stamping operations. As demonstrated throughout this guide, proper force analysis impacts tooling design, press selection, energy consumption, and final product quality. China Custom Stamping, a professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturer in China, combines theoretical calculations with practical experience to deliver optimized stamping solutions across industries.
By understanding the detailed components of blanking force—from basic shear calculations to advanced dynamic considerations—manufacturers can achieve significant improvements in productivity and cost-efficiency. The future of blanking force calculation lies in the integration of traditional engineering principles with cutting-edge computational methods, an area where China Custom Stamping continues to lead as a professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturer in China’s evolving industrial landscape.
For complex projects requiring expert blanking force analysis, consult China Custom Stamping’s engineering team to leverage our professional metal stamping and deep drawing manufacturing expertise in China’s competitive market. Our combination of theoretical knowledge and practical experience ensures optimal force calculations for your specific application requirements.